Ping
Created on 17 September, 2025 • Checker tools • 121 views • 4 minutes read
A Complete Guide to Testing Network Connectivity
Ping: Understanding Network Latency and Internet Speed
What Is Ping?
Ping is a simple yet powerful tool used to test the speed and stability of a network connection. It measures how long it takes for a small packet of data to travel from your computer to another server and back.
In technical terms, it calculates latency — the time delay in communication between two devices on the internet. The result is measured in milliseconds (ms), and the lower the number, the faster your connection.
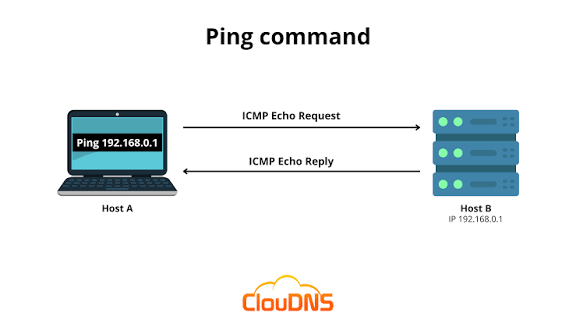
When you send a ping request, your device sends a small signal (known as an ICMP Echo Request) to a specific server. If the server responds, it sends back an ICMP Echo Reply. The time between these two actions is your ping result.
Why Is Ping Important?
1. Testing Internet Connection Quality
Ping helps users understand how responsive their internet connection is. If websites or online games feel slow or laggy, running a ping test can show whether the issue is caused by your connection or the server you’re reaching.
2. Gaming and Streaming Performance
For gamers, ping is everything. A lower ping means faster reaction times in online games, while higher ping causes lag and delays. Streaming platforms also depend on stable, low ping for smooth playback.
3. Network Troubleshooting
Ping is often the first step in diagnosing network issues. If you can’t reach a website, sending a ping helps determine if the problem is your network, the server, or a routing issue.
4. Server Monitoring and Maintenance
Website owners and IT professionals use ping to monitor server uptime. A server that fails to respond to ping requests may be offline, overloaded, or misconfigured.
What Does Ping Tell You?
A ping result provides key data points about your connection:
- Latency (ms): The time taken for the data round trip.
- Packet Loss: Indicates whether some data didn’t reach its destination.
- Jitter: The variation in latency — consistent ping is better than fluctuating times.
- Destination IP or Host: The server or domain you’re testing.
By analyzing these results, users can better understand the quality and reliability of their network.
Ideal Ping Ranges
Ping Time (ms)Connection QualityUser Experience0–30 msExcellentUltra-smooth gaming and video calls31–60 msGoodSmall delays, barely noticeable61–100 msFairSlight lag during online activities101–200 msPoorNoticeable delay or stutter200+ msVery PoorHigh lag, slow performance
The closer your ping is to zero, the better your connection experience.
What Causes High Ping?
There are several factors that can increase ping:
- Slow Internet Speeds: Limited bandwidth causes delays.
- Distance to Server: The farther the server, the longer the signal travel time.
- Wi-Fi Interference: Weak or unstable wireless signals increase latency.
- Network Congestion: Too many devices using the same network slow down responses.
- Background Apps: Streaming, updates, or downloads running in the background can affect ping.
Understanding these causes helps you make adjustments to improve overall speed and performance.
How to Check Ping
1. Online Tools
Websites such as Speedtest.net or Fast.com automatically measure ping, upload, and download speeds.
2. Command Line Tools
Advanced users can test ping directly from their computer using the built-in ping command. For example, typing ping google.com sends a test signal to Google’s servers and reports the result.
3. Gaming Platforms and Apps
Most online games and streaming services display ping in their network settings. You can switch to a nearby server for faster performance.
How to Reduce Ping
If you experience high ping, try these solutions:
- Use a Wired Connection: Ethernet cables are faster and more stable than Wi-Fi.
- Close Background Apps: Stop downloads, updates, and unnecessary tabs.
- Restart Router or Modem: Refreshing your connection can improve response time.
- Choose a Closer Server: Select a regional server to minimize distance delays.
- Upgrade Your Internet Plan: If lag persists, contact your ISP for a higher-speed plan.
Following these steps can greatly reduce latency and make your online experience smoother.
Ping in Everyday Use
Ping is used by a wide range of people — not just tech professionals:
- Gamers: To keep online matches responsive.
- Web Developers: To check server uptime.
- Network Engineers: To identify routing problems.
- Regular Users: To troubleshoot slow internet.
Even your smartphone apps and smart devices constantly “ping” servers to stay connected, check for updates, and sync data in real time.
Privacy and Ping Monitoring
While ping itself doesn’t reveal personal data, constant monitoring can help companies and users understand network reliability. Many organizations use ping tests to track service health without accessing user information — keeping it safe and compliant with data privacy regulations.
The Future of Low-Latency Networks
As we move into 2025, the world is shifting toward ultra-low latency technologies such as 5G, fiber optics, and edge computing. These innovations bring data closer to users, drastically reducing ping and improving performance for online gaming, virtual reality, cloud computing, and AI-driven applications.
Lower ping means faster decisions, smoother communication, and a better-connected world.
Conclusion
Ping may sound like a small technical term, but it plays a huge role in how we experience the internet every day. It measures the heartbeat of your connection — the delay between request and response.
Whether you’re testing a slow website, monitoring your server, or trying to win an online game, understanding ping helps you diagnose issues and optimize your digital performance.
By keeping your ping low, you ensure smoother connections, faster responses, and a more reliable online experience — something every user and business can benefit from.
Popular posts
-
Random number generatorGenerator tools • 171 views
-
Emojis removerText tools • 168 views
-
Lorem Ipsum generatorGenerator tools • 165 views
-
Reverse lettersText tools • 159 views
-
Old English text generatorText tools • 158 views