HTHP headers lookup
Created on 17 September, 2025 • Checker tools • 127 views • 4 minutes read
A Complete Guide to Inspecting Website Headers
HTTP Headers Lookup: Understanding How Web Requests Work
What Is an HTTP Header Lookup?
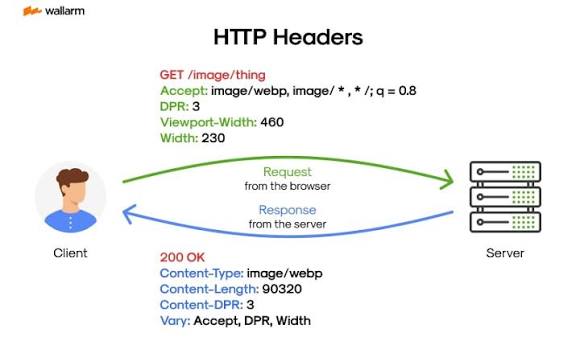
An HTTP Headers Lookup is a process used to view the hidden communication between your browser and a website’s server. Every time you visit a webpage, your browser sends a request and receives a response. These messages contain important data known as HTTP headers — key-value pairs that describe how content should be delivered, cached, or secured.
An HTTP Headers Lookup tool lets you inspect these details easily. By checking headers, developers, website owners, and security professionals can better understand how their sites interact with browsers and other web services.
Why Are HTTP Headers Important?
HTTP headers play a vital role in how websites load, perform, and protect user data. They control everything from content type and caching rules to authentication and redirection.
Here’s why they matter:
1. Website Performance
Headers manage caching and compression, helping websites load faster and reduce bandwidth use.
2. Security
HTTP headers like Content-Security-Policy (CSP) and Strict-Transport-Security (HSTS) protect users from cyberattacks such as data interception or code injection.
3. Debugging and Troubleshooting
If a webpage isn’t working correctly, checking headers can reveal issues such as missing resources, incorrect redirects, or invalid responses.
4. SEO Optimization
Headers like 301 Redirects and Canonical URLs help search engines understand how pages should be indexed, improving SEO performance.
5. User Experience
By properly managing headers, developers can ensure smoother browsing experiences, fewer errors, and faster responses.
What Information Does an HTTP Header Contain?
An HTTP header is divided into two main types — Request Headers and Response Headers.
Request Headers
These are sent from your browser to the web server when you visit a page. Common examples include:
- Host: The domain name of the website being requested.
- User-Agent: Information about the browser and device used.
- Accept: Specifies which content types (like HTML or JSON) are supported.
- Referer: Indicates the previous page the user came from.
- Accept-Language: The preferred language for the content.
Response Headers
These come from the server to your browser after receiving your request. Common response headers include:
- Content-Type: Defines the format of the returned content (HTML, JSON, text, etc.).
- Server: Reveals the software running on the web server (like Apache or Nginx).
- Cache-Control: Determines how and for how long content can be stored.
- Set-Cookie: Sends cookies to the browser for session management or tracking.
- Location: Used for page redirection.
Together, these headers help your browser and the server communicate effectively.
How Does HTTP Header Lookup Work?
When you perform an HTTP Headers Lookup, your request goes through a lookup tool that:
- Sends a small HTTP request to the website’s server.
- Waits for the server to respond with header information.
- Displays both the request and response headers in a readable format.
Most lookup tools also show the HTTP status code, such as:
- 200 OK: Page loaded successfully.
- 301 Moved Permanently: The page was redirected.
- 404 Not Found: The page doesn’t exist.
- 500 Internal Server Error: The server encountered a problem.
This information helps website owners quickly understand what’s happening behind the scenes of every web request.
Practical Use Cases for HTTP Headers Lookup
1. Website Optimization
Developers use header lookups to fine-tune caching, compression, and redirect settings for faster loading times.
2. Security Analysis
Cybersecurity teams review headers to check if SSL/TLS, CSP, or HSTS are properly configured to secure the website.
3. Debugging Redirects and Errors
HTTP headers reveal redirect loops, outdated links, or misconfigured status codes that can break user journeys.
4. SEO Audits
Headers help SEO professionals confirm if canonical tags, redirections, and response codes are properly set up for search engines.
5. API Testing
Developers testing REST APIs use HTTP header lookups to verify content types, tokens, and response codes for each request.
Common HTTP Header Fields Explained
Header NamePurposeExampleContent-TypeDescribes the type of contenttext/htmlCache-ControlDefines caching rulesno-cacheServerShows server typenginxSet-CookieManages browser cookiessessionid=abc123LocationRedirects to a new pagehttps://example.com/new-pageContent-EncodingEnables compressiongzipX-Frame-OptionsPrevents clickjackingDENYAccess-Control-Allow-OriginManages cross-domain access*
These headers form the foundation of how modern websites communicate securely and efficiently.
How to Perform an HTTP Headers Lookup
Performing an HTTP header lookup is easy and doesn’t require coding skills. Here are common methods:
1. Online Tools
Free lookup tools like websniffer.cc, httpstatus.io, or tools.keycdn.com/http2-test allow you to view complete header information for any website.
2. Browser Developer Tools
In browsers like Chrome or Firefox, press F12 → go to the Network tab → refresh the page → and click on a request to view headers.
3. Command Line
Advanced users can use terminal commands like curl -I https://example.com to fetch only the HTTP response headers.
4. API Integrations
Some APIs provide header lookup capabilities that can be automated for monitoring or analysis.
Limitations of HTTP Header Lookup
Although very useful, header lookups have some limitations:
- Server Restrictions: Some servers block automated requests for security reasons.
- Dynamic Content: Websites using CDNs may display different headers depending on region.
- Privacy Concerns: Certain headers reveal software or version details that could be exploited if not properly secured.
Future of HTTP Headers and Web Communication
As web technologies evolve, HTTP headers are becoming even more powerful and privacy-focused. With HTTP/3 and QUIC protocols, headers now travel faster and more securely over encrypted channels.
Future browsers and servers will continue using headers to improve data protection, load speed, and AI-driven optimization. For website owners and developers, understanding headers will remain essential to maintaining transparency and trust online.
Conclusion
An HTTP Headers Lookup provides a behind-the-scenes view of how your website communicates with users. It’s an essential tool for developers, SEO professionals, and cybersecurity experts alike.
By analyzing headers, you can identify performance issues, strengthen website security, and ensure your pages deliver the best experience possible.
Whether you’re maintaining your business website, personal blog, or profile site like ProfileLinks.xyz, performing regular header lookups helps keep your online presence secure, fast, and reliable.
Popular posts
-
Random number generatorGenerator tools • 171 views
-
Emojis removerText tools • 168 views
-
Lorem Ipsum generatorGenerator tools • 165 views
-
Reverse lettersText tools • 159 views
-
Old English text generatorText tools • 158 views